Understanding the Difference Between Low and High Threshold Strategies
Written by Aaron Swanson SFMA
(This guest post is authored by FMS/SFMA Certified PT Aaron Swanson. It was originally published on aaronswansonpt.com and is republished here with permission).
Understanding the difference between low and high threshold strategy is a very important part of rehab and training. If a patient is using the wrong strategy for the task they will not only be inefficient, but they can make the injury worse and cause more harm.
Unfortunately, this has happened to all of our patients at one time or another. We give them a simple exercise like single leg balance, look away for a second, and turn back to see them holding their breath and violently flailing their arms to keep their balance. They’re not developing stability, they’re just using a dysfunctional high-threshold strategy to teach their body how to compensate with the wrong muscles.
If you understand the difference between the 2 strategies, you can prevent this from happening to your patients.
Quick Definitions:
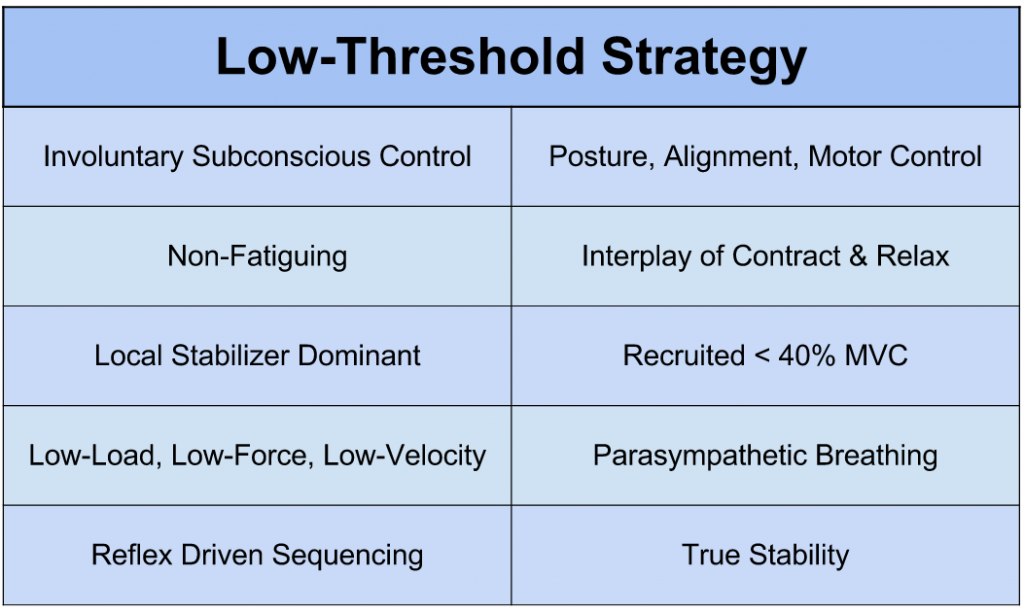
Low-Threshold Strategy: Slow, tonic, local stabilizer, stabilizing muscle contractions that are for low-load tasks and reflexive postural control. This is necessary for joint centration.
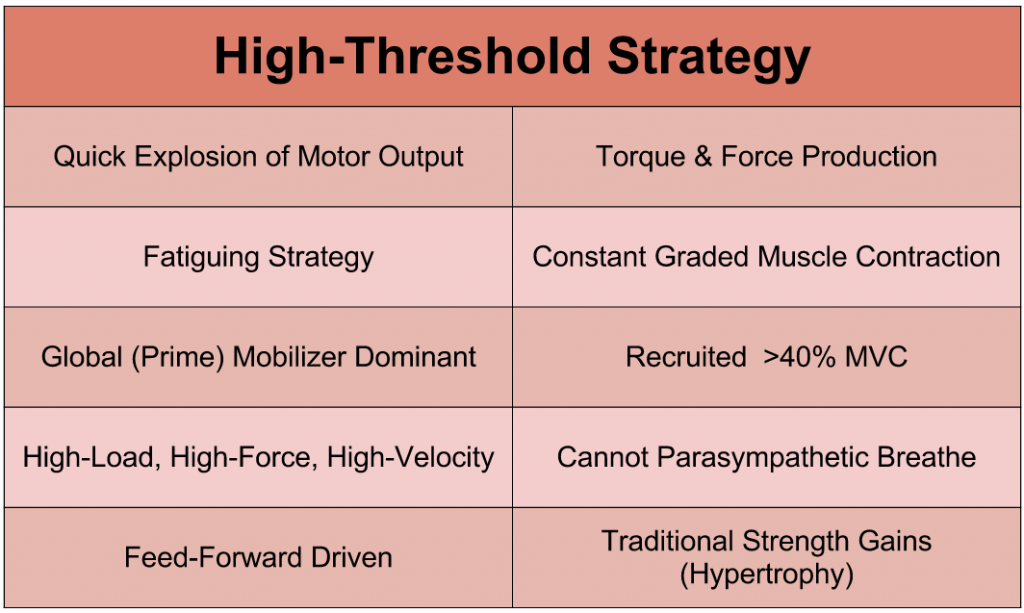
High-Threshold Strategy: Fast, phasic, prime mover, global mobilizer, mobilizing muscle contractions that are for high-load tasks and force production. This is necessary for strength training.
5 Major Points
- The difference between high and low-threshold is one of the most important parts of the exercise continuum
- Low-Threshold must occur prior to High-Threshold to stabilize and centrate the body
- High-Threshold is necessary, but can become dysfunctional with poor training strategies
- Assess for threshold strategy by looking at breathing, posture, and alignment
- Build programs to encourage a fundamental low-threshold strategy before starting high-threshold exercises
Motor Units & Threshold Strategies
Motor Unit
High and low threshold strategy refers to the type of motor unit activity driving a task. These motor units are responsible for muscle contractions. The type of motor units recruited for a task are based on many different factors including: muscle fiber type, role of muscle, motor pattern, firing rate, and recruitment threshold.
Threshold Strategies
It’s important to understand that most local stabilizing muscles have a higher portion of low-threshold motor units, where as global moving muscles have a higher portion of high-threshold motor units. Further more, motor units are recruited sequentially from low to high. It’s the body’s way of being efficient and trying to perform a task with the easiest motor program possible. So before high-threshold motor units are recruited, all of the other motor units must be recruited (high-threshold on top of low-threshold). This increases the mechanical advantage of the global movers and centrates the joint, thus making it more efficient to perform the task.
Low-Threshold Strategy MUST be recruited before High-Threshold Strategy.
Exercise and Thresholds
To put it in perspective you can look at single leg balance. You should be able to stand on one leg using a low-threshold strategy. However, if you add medicine ball throws or step-ups to a single leg stance you are going to have to use a high-threshold strategy on top of a low-threshold strategy. A low-threshold strategy alone is not strong enough to create enough force to throw a heavy medicine ball.
Low-Threshold & High-Threshold
Before you go crazy trying to label each movement and exercise, it’s important to note that this is a continuum. Not every movement is going to be exclusively one type of motor strategy.

Low-Threshold
Working within the edge of ability and gaining fundamental stability is paramount for developing efficient stability and power. Unfortunately many clinicians and trainers overlook this low-threshold motor strategy.
Here’s an example. I had an acute low back patient who was deadlifting 350 pounds. He could touch his toes, passed the ASLR test, his hips were strong, and he could hold a plank for hours. But when I took him through some low-threshold developmental stability patterns he started shaking all over the place. After he developed some low-threshold stability he went back to pain-free deadlifting and improved his PR by 20 pounds in the next month. It’s not always this extreme, but shows a great example of how joint centration goes beyond rehab.
So there are 2 ways you can sell this to your patients:
Optimist: If you are really strong without a low-threshold motor program, then imagine how much stronger you would be with one.
Pessimist: If your strong without a low-threshold motor program, then all you did was strengthen your compensations and poor movement patterns.
High-Threshold
Some people use the term high-threshold strategy to define a dysfunctional motor strategy. I feel that this can be a little misleading and give high-threshold motor patterns a bad rap. If athletes didn’t use high-threshold strategies they wouldn’t be able to accomplish the amazing physical feats we see on Sports Center’s Top 10. And without high-threshold strategies our Top 10 would just be a bunch of trick pool shots and geriatric shuffleboard.
What Goes Wrong?
The body moves very efficiently when the low-threshold precedes the high-threshold. It’s when people skip the low-threshold step that things start to go very wrong. This dysfunctional high-threshold only strategy will plague the body compensations and inefficient movement.
When the body fatigues and the local stabilizers stop firing, the body goes into a dysfunctional high-threshold strategy. This is filled with poor movement patterns. To make matters worse, it teaches the body how to incorrectly use global mobilizing muscles (as movers AND stabilizers). So now these muscles are always on and always trying to do everything, even for low-load activities.
Just like anyone that is worked twice as hard, these muscles get very unpleasant. They lock up, have overdeveloped tone, become fibrotic, have decreased blood supply (from being contracted all the time) and become over facilitated.
Cranking on these muscles may provide temporary relief. But to solve the problem you need to go to the low-threshold strategy that isn’t firing. Other wise the viscous cycle will continue.
High-Threshold Strategy is a Dysfunctional Pattern When:
- Used in Substitution of Low-Threshold
- Cannot Turn Muscles “Off” (Results in Splinting, Not Stabilizing)
- Global Mobilizing Muscles Have to Move AND Stabilize
- Places the Body in Poor Alignment / Posture
- Sacrifices Mobility for Force Production
So how do you assess for which strategy is being used?
The simple answer is breathing. 99% of the time breathing strategy it will match up with their threshold strategy.
The Threshold-Breathing-Continuum: Parasympathetic diaphragm breathing is used in low-threshold strategies. Breath holding and valsalva is used in high-threshold strategies.
Another give away for dysfunctional threshold strategy is poor alignment/posture. If someone can’t use a low-threshold strategy they’ll compensate with a high-threshold strategy and the global mobilizing muscles will pull the body out of optimal positioning (centration).
So What Do You Do Now…?
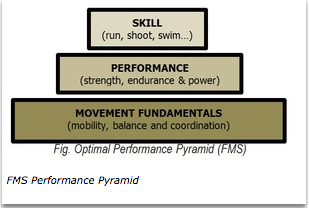
FMS Performance Pyramid
The FMS Performance Pyramid provides a great picture of how to balance your plan of care (or training) in terms of human performance. Much like the low before high-threshold principle, this pyramid emphasizes the fundamental mobility balance, and coordination.
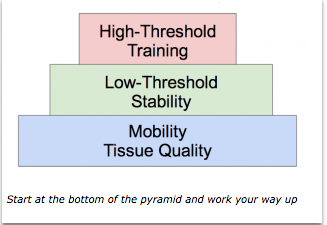
My Threshold Pyramid
It’s important to first consider mobility before threshold strategies. Mobility and tissue quality is a priority before stability and movement. Trying to force patients through mobility deficits will only feed into their movement pattern dysfunction. Once you have resolved or made a change in their mobility, you should then move towards threshold training.
Since the normal firing pattern is low-threshold before high-threshold, you should probably train your patients the same way. To do this, simply make sure your patient can perform low-threshold strategies independent of load, force, or movement. After this is accomplished you can add in the load, force, or movement and work towards more high-threshold type of strengthening exercises.
Once they are efficient with the low-threshold patterns don’t throw them away and forget about them. They’re great for warm-ups, CNS resets, starting positions, or active rest.
Examples of Low-Threshold → High-Threshold:
Core: Soft Rolling → Hard Rolling
Shoulder: Bottom-Up Kettlebell Screwdriver → Single Arm Rows
Hip: Quadruped Alt UE/LE → Deadlift
Bottom Line
There’s already enough to think about when selecting exercises (pathology, movement pattern, biomechanics, kinesiology, anatomy, etc.). And it sucks to add more to the list. But if your patient is using a dysfunctional high-threshold strategy the rest of the list doesn’t matter. By keeping tabs on the threshold strategy your exercise prescription will only be more effective.
Related Resources
Please login to leave a comment
6 Comments
-

Larry 3/29/2016 1:21:59 PM
All trainers should read this article
-

John Zieour 3/31/2016 2:59:29 PM
Nice article Aaron, any advice or direction for someone looking to learn more about " how to evaluate, control and teach proper diaphragmatic breathing?"
-
Kyle Barrow FMS 3/31/2016 2:59:29 PM
John,
These are some great resources:"Light on Yoga" by Lyengar"Close Your Mouth" by Peter Mckowe"Multidisciplinary Approach to Breathing Pattern Disorders" by Chaitow
Our FMS level 2 course focus on breathing as a gateway into sympathetic vs. parasympathetic balance, stress, and efficacy in the body. We teach you basic breathing screens for proper diaphragmatic breathing, provide corrective drills, and learn to continuously evaluate breathing during corrective and training exercises.
Please take a look at our exercise library for corrective techniques for dysfunctional breathing. -

Jason A Glass 4/5/2016 5:31:40 PM
Great article Aaron. Very well laid out. I love the topic and I discuss this topic in depth with Dr. Mike Voight on the Coach glass Podcast http://www.jasonglassperformancelab.com/2014/09/17/826/ I agree with your clarification and would add that High Threshold can also include activities with multi jointed, multi-plane movement with high coordination complexity. Not corrective and not strength training but all the exercises and movements we use in between those 2 elements. Even though Strength and Power require High Threshold strategies I don't classify them as High Threshold Exercises. I just call them Strength and Power and leave the terminology of High Threshold for the non loaded, complex movements that live in the gap. Please understand that this is not in anyway a criticism it is just semantics. We teach these High Threshold exercises in our TPI Level 2/3 Fitness certification classes as a transition from the 4x4 corrective matrix into the strength and power phases of our programming. Again, great article! Cheers!
-

Clare 4/5/2016 5:30:30 PM
Really interesting Sounds really similar to The Performance Matrix (TPM).
I think their screening is based more on this..Thanks for sharing this. -

Kristen Carter 4/4/2016 1:30:01 PM
Thanks for a great article. Makes it easier to explain to my clients why we are starting so slow or small, which is sometimes a hard sell. Our industry has to get used to presenting results as something that does not happen over night, and needs to be thoughtfully and professionally guided. Will check out your library for ways to mobilize prior to low threshold training. Thanks for sharing!